International Council of Nations
International Council of Nations
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
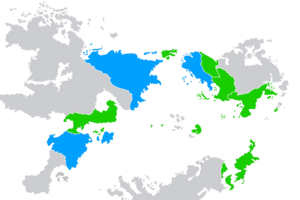 Map showing the member states of the International Council of Nations. Blue - Big Three : Green - Member Light Green - Observer : Light Grey - Non-member | |||||
| Headquarters | 1 ICN Plaza, Juneau, Cascadian Capital Territory, Cascadia (International Territory) | ||||
| List of Languages | |||||
| Type | Intergovernmental Organization | ||||
| Membership | x member states x observer States | ||||
| Leaders | |||||
• Secretary-General | Savita Mutti | ||||
| Establishment | |||||
• ICN Charter signed | 20 April 1984 | ||||
• Charter Entered Into Force | 20 April 1984 | ||||
Website www.icn.org | |||||
The International Council of Nations, or ICN informally, is an intergovernmental organization based in Juneau whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and serve as a canter for harmonizing the actions of nations. The ICN serves as a platform for member states to engage in diplomatic discussions, negotiate agreements, and collaborate on matters of mutual interest.
History
The International Council of Nations was established on date with the signing of the Treaty in the city of Juneau, Cascadia. The treaty was ratified by the founding member states, FOUNDING MEMBERS, marking the official formation of the ICN. The organization was envisioned as a forum where nations could come together to foster peace, stability, and prosperity on a global scale.
Background
Founding
Objectives
The International Council of Nations has the following key objectives:
- Promoting international peace and security
- Facilitating economic cooperation and sustainable development
- Protecting human rights and fostering social progress
- Addressing global challenges such as climate change, poverty, and inequality
- Encouraging cultural exchange and preserving cultural heritage
- Enhancing international cooperation in the fields of science, technology, and education
Structure and Governance
The International Council of Nations operates on the principle of sovereign equality, where each member state has an equal voice and voting rights. The organization is led by a Secretary-General, who is elected by the member states for a fixed term. The Secretary-General acts as the chief administrative officer and represents the ICN in international forums. The ICN also has a group of 3 nations aptly named The Big 3. These 3 nations may veto any ICN general assembly or security council resolutions for any reason.
The ICN maintains a headquarters in Juneau, Cascadia, which serves as the central hub for its activities. Various specialized agencies, committees, and working groups are established within the organization to focus on specific areas of concern. These bodies work collaboratively to analyze global challenges, propose solutions, and implement policies to address them.
| ICN General Assembly — Deliberative assembly of all ICN member states — |
ICN Secretariat — Administrative organ of the ICN — |
International Court of Justice — Universal court for international law — | ||
|
|
|
Membership
Membership in the International Council of Nations is open to all sovereign states that are willing to uphold the principles and objectives of the organization. Currently, the ICN boasts XX member states from diverse geographical regions. Prospective nations must submit an application for membership, which is reviewed and approved by existing member states through a consensus-based decision-making process.
Full Members
| Flag | Member State | Date of Admission | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cascadia | Founding Date | One of the big three. Founding member. | |
| Central Exoña | |||
| Dargentia | Founding Date | One of the big three. Founding member. | |
| Khozhlod | Founding Date | One of the big three. Founding member. | |
| Nordmarken-Flachland | |||
| Xuka |
Observers
See Also
Donjon
Intergovernmental Organization


